Key Learnings
BIM Introduction
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is an intelligent 3D model-based process that gives architecture, engineering, and construction professionals the insights and tools to efficiently plan, design, construct, and manage buildings and infrastructure.
BIM offers a 3D model-based approach that provides more detailed, coordinated, and accurate information compared to traditional 2D CAD, which only represents buildings in flat, two-dimensional drawings.BIM is beneficial for architects, civil engineers, structural engineers, MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) professionals, construction managers, and facility managers. It enhances collaboration and communication across various disciplines in construction and design.
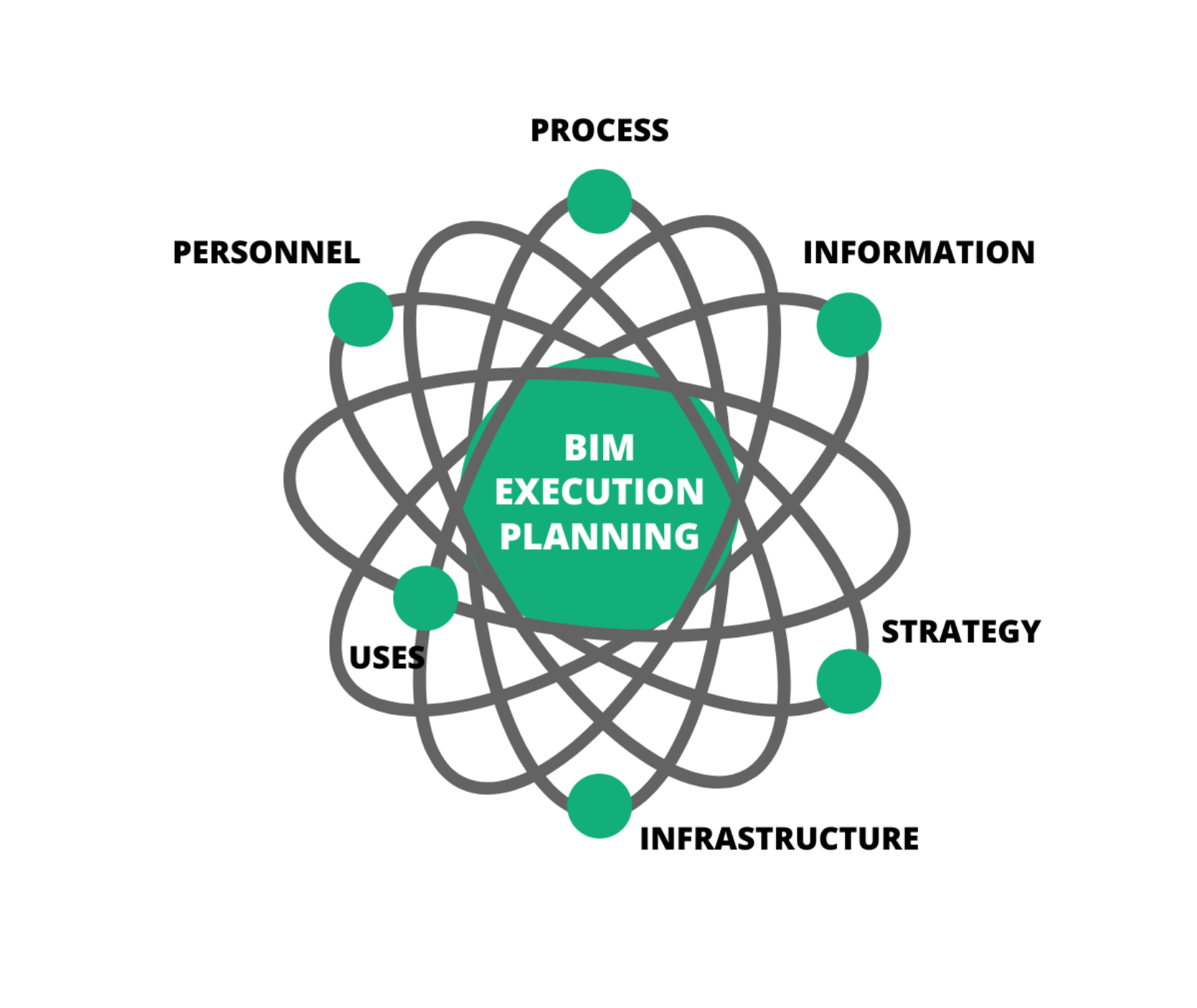
BIM Execution Plan(BEP)
A BIM Execution Plan (BEP) is a detailed document outlining how Building Information Modeling (BIM) will be implemented throughout a project’s lifecycle. It defines the roles, responsibilities, processes, and standards for all stakeholders involved in a BIM project.
A BIM Execution Plan ensures that all team members work efficiently and collaboratively, reducing project risks, streamlining communication, and ensuring consistency in the use of BIM standards and workflows. It helps to avoid miscommunication, delays, and rework.The BIM Manager or BIM Coordinator is usually responsible for creating the BEP, in collaboration with the project team, including architects, engineers, and contractors. All stakeholders should contribute to ensure the plan is comprehensive and meets project needs.

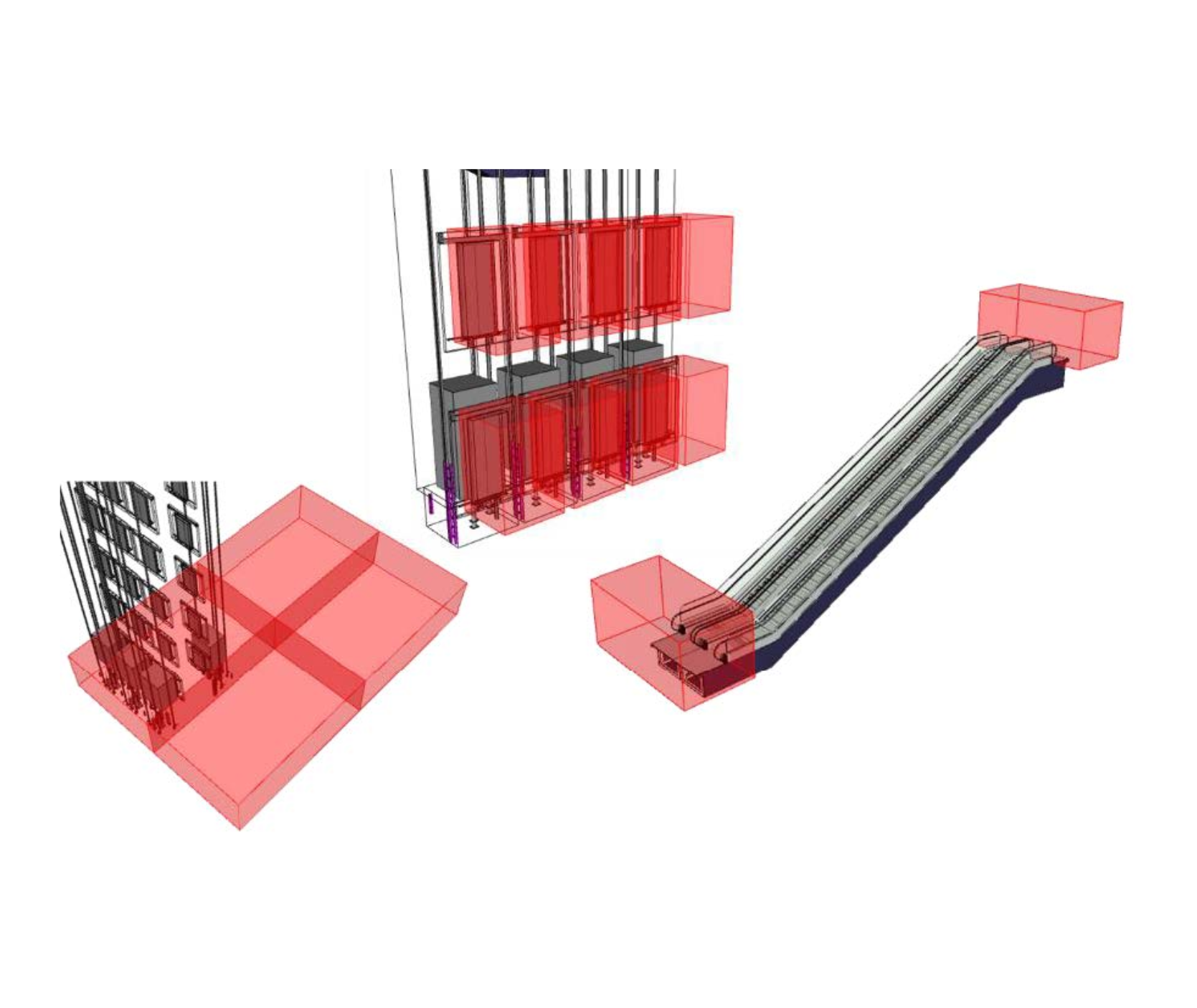
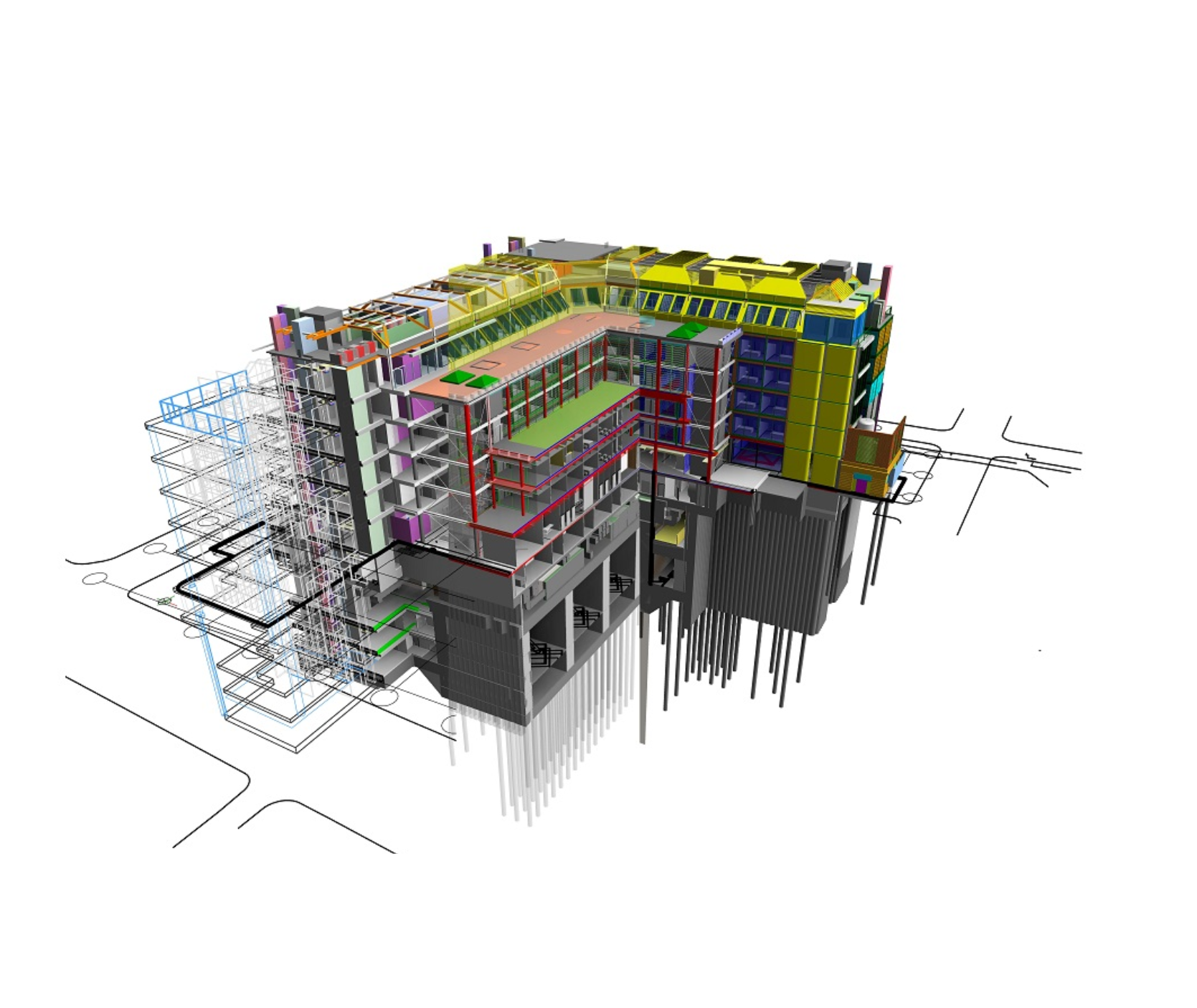
3D Modelling
3D modeling is the process of creating a three-dimensional representation of any object or surface using specialized software. This virtual model can be used in various industries like architecture, engineering, gaming, and animation.Some of the most popular 3D modeling software tools include Autodesk 3ds Max, Blender, SketchUp, Rhino, and Maya. Each tool has its specific use cases and strengths depending on the industry.In architecture and engineering, 3D modeling is used to visualize buildings, infrastructure, or mechanical systems. It allows designers to simulate real-world scenarios, test design options, and ensure accuracy before construction or production.
Industries such as architecture, engineering, manufacturing, gaming, animation, healthcare (for medical imaging and simulations), and automotive design all benefit from 3D modeling techniques.
4D Simulations
4D simulation refers to a construction management process that integrates 3D models with the time factor (schedule) to create a dynamic visualization of the construction sequence. It helps project teams understand how a building or infrastructure project will be constructed over time.4D simulation allows project managers to visualize the construction schedule and identify potential conflicts or delays before the project begins. It helps in optimizing workflows, resource allocation, and sequencing to ensure smoother execution.
4D simulation is primarily used in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries. It is especially valuable in large-scale infrastructure projects like highways, bridges, airports, and commercial buildings.Popular software tools used for 4D simulation include Autodesk Navisworks, Synchro, and Bentley Systems. These tools integrate 3D models with project schedules to create a time-based simulation.